Secure Distal Fixation
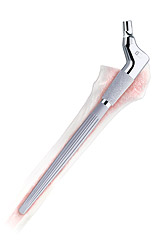 The ZMR Taper Revision Hip Prosthesis is designed to achieve secure distal fixation* in the femur using a sharply splined and tapered distal stem with a roughened Tivanium® Alloy surface. The tapered distal stem is designed to wedge into the femoral medullary canal, transferring axial and bending forces, while the splines are press-fit into bone to provide rotational stability. The roughened Tivanium Alloy surface allows bone ongrowth.1-3 The modular proximal bodies and distal stems provide many sizing options to help achieve anatomic restoration.
The ZMR Taper Revision Hip Prosthesis is designed to achieve secure distal fixation* in the femur using a sharply splined and tapered distal stem with a roughened Tivanium® Alloy surface. The tapered distal stem is designed to wedge into the femoral medullary canal, transferring axial and bending forces, while the splines are press-fit into bone to provide rotational stability. The roughened Tivanium Alloy surface allows bone ongrowth.1-3 The modular proximal bodies and distal stems provide many sizing options to help achieve anatomic restoration.
*For femurs with inadequate proximal support, the ZMR XL Hip System should be used.
References
- Feighan JE, Goldberg VM, Davy D, et al. The influence of surfaceblasting in the incorporation of titanium-alloy implants in a rabbit intramedullary model. J Bone Joint Surg. 1995;77-A;9:1380-1395.
- Zweymuller KA, Lintner FK, Semlitsch MF. Biologic fixation of a press-fit titanium hip joint endoprosthesis. Clin Orthop. 1988;235:195-206.
- Lintner F, Zweymuller, Brand G. Tissue reactions to titanium endoprosthesis. J Arthroplasty. 1986;1;3:183-195.
Indications
The ZMR Hip Prosthesis is indicated for cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients whose bone stock is of poor quality or inadequate for other reconstruction techniques as indicated by deficiencies of the femoral head, neck, or portions of the proximal femur. Arthroplasty should be performed only when more conservative methods of treatment have failed to provide symptomatic relief or when there is progressive disability.
Information for Use
Special instruments are available and necessary to assemble, disassemble, and accurately install the implant components.
Contraindications
Contraindications include:
- Use of this device when a less invasive procedure would be sufficient
- Skeletal immaturity
- Loss of abductor musculature in the affected limb
- Poor bone stock (e.g., steroid-induced metabolic bone disease)
- Poor skin coverage around the hip joint
- Neuromuscular disease (e.g., Charcot’s joint) in the affected limb







