Güvenli Distal Fiksasyon
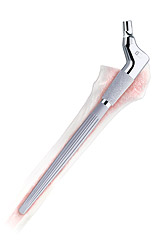 ZMR Protez Konik Revizyon Kalça ve pürüzlü bir keskin yivli ve konik distal stem kullanarak femur güvenli distal fiksasyon * ulaşmak için tasarlanmıştır Tivanium ® Alaşım yüzey. Spline rotasyonel stabiliteyi sağlamak için kemik içine press-fit ise konik distal stem, eksenel ve eğilme kuvvetlerine transfer, femur medüller kanal içine kama için tasarlanmıştır. PürüzlüTivanium Alaşım yüzey kemik ongrowth verir. 1-3 modüler proksimal gövde ve distal gövde anatomik restorasyonu ulaşmanıza yardımcı olacak pek çok boyutlandırma seçenekleri sunar.
ZMR Protez Konik Revizyon Kalça ve pürüzlü bir keskin yivli ve konik distal stem kullanarak femur güvenli distal fiksasyon * ulaşmak için tasarlanmıştır Tivanium ® Alaşım yüzey. Spline rotasyonel stabiliteyi sağlamak için kemik içine press-fit ise konik distal stem, eksenel ve eğilme kuvvetlerine transfer, femur medüller kanal içine kama için tasarlanmıştır. PürüzlüTivanium Alaşım yüzey kemik ongrowth verir. 1-3 modüler proksimal gövde ve distal gövde anatomik restorasyonu ulaşmanıza yardımcı olacak pek çok boyutlandırma seçenekleri sunar.
* Yetersiz proksimal destek femurlar için, ZMR XL Kalça Sistemi kullanılır.
Referanslar
- Feighan JE, Goldberg VM, Davy D, et al. Bir tavşan intramedüller modelinde titanyum alaşımlı implantlar şirketleşmesinde surfaceblasting etkisi. J Bone Joint Surg . 1995; 77-A; 9:1380-1395.
- Zweymuller KA, Lintner FK, Semlitsch MF. Eklem endoprotez. Kalça a press-fit titanyum Biyolojik fiksasyon Clin Orthop. 1988, 235:195-206.
- Lintner F, Zweymuller, titanyum endoprotezi. Brand G. Doku reaksiyonları J Artroplasti . 1986; 1; 3:183-195.
Indications
The ZMR Hip Prosthesis is indicated for cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients whose bone stock is of poor quality or inadequate for other reconstruction techniques as indicated by deficiencies of the femoral head, neck, or portions of the proximal femur. Arthroplasty should be performed only when more conservative methods of treatment have failed to provide symptomatic relief or when there is progressive disability.
Information for Use
Special instruments are available and necessary to assemble, disassemble, and accurately install the implant components.
Contraindications
Contraindications include:
- Use of this device when a less invasive procedure would be sufficient
- Skeletal immaturity
- Loss of abductor musculature in the affected limb
- Poor bone stock (e.g., steroid-induced metabolic bone disease)
- Poor skin coverage around the hip joint
- Neuromuscular disease (e.g., Charcot’s joint) in the affected limb







